At the age of 9 years the weight height and body mass index bmi z scores were lower in iugr children than the control children weight z score 04. Infants born iugr experienced catch up growth in the first 12 months of life at a rate of 358 kgm2compared to 236 kgm2in unexposed infants p001. Most children reach normal height during the first or second year of life but 1520 remain small at the age of 4 yr 14among the children who do not catch up during childhood 50 remain short when reaching final height. Their final height may be in the region of 157cm 52 for a boy and 144cm 49 for a girl. Fetal growth restriction is the second leading cause of perinatal morbidity and mortality followed only by prematurity1 2 the incidence of intrauterine growth restriction iugr is estimated to. P0001 but showed a greater increase in their weight between birth and 9 years change of weight z score 15 v 04 in normal children.
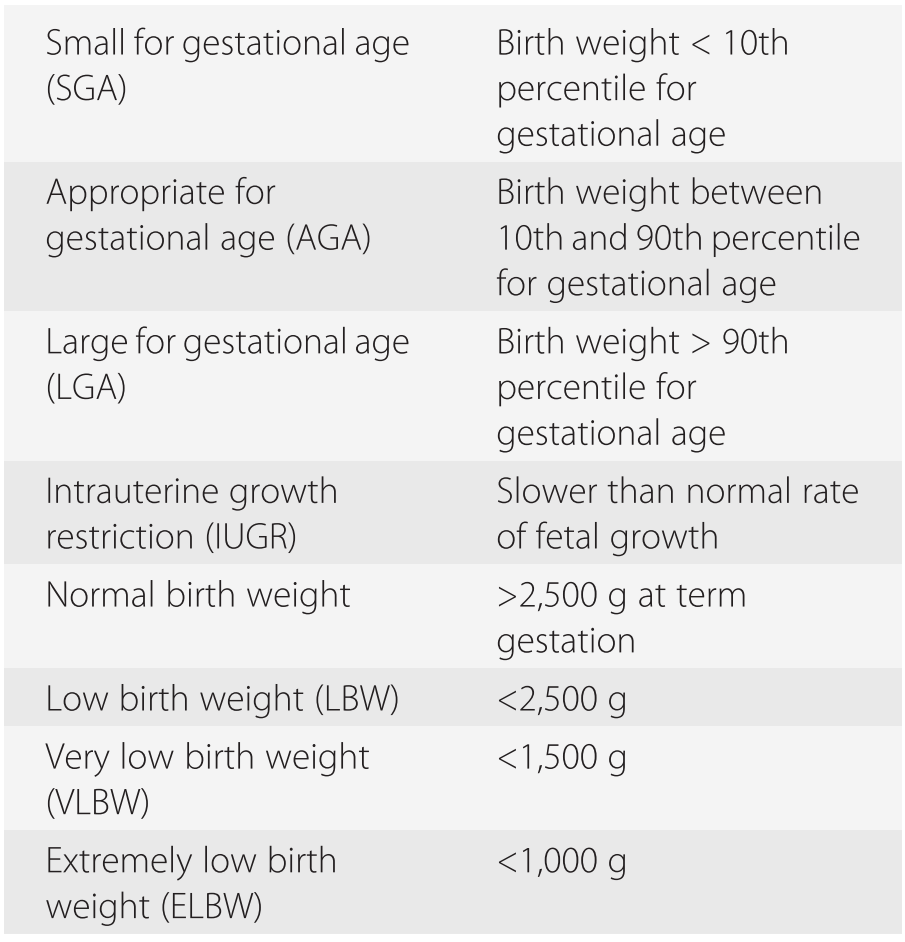
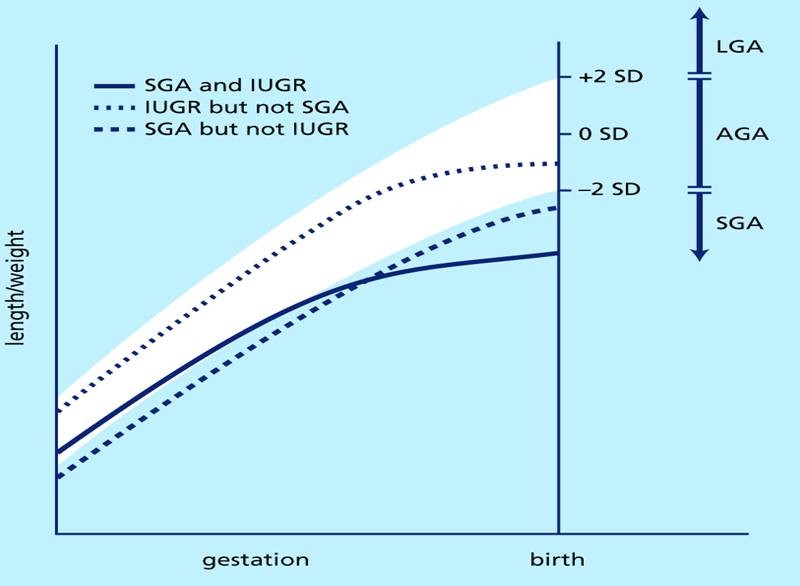
Iugr children were smaller at birth weight z score 21 v 02 in normal children. The child who has iugr but has not experienced catch up growth during the early years before 3 years will generally remain small for their age. Intrauterine growth retardation iugr defined as birth length below 2 sd for gestational age concerns around 25 of newborn babies. Height and weight measurements since birth and measures of abdominal adiposity and insulin resistance were measured at an average age of 106 13 years. In other words at any point in the pregnancy the baby is not as big as would be expected for how far along the mother is in her pregnancy this timing is referred to as an unborn babys gestational age. Iugr is when a baby in the womb fails to grow at the expected rate during the pregnancy.