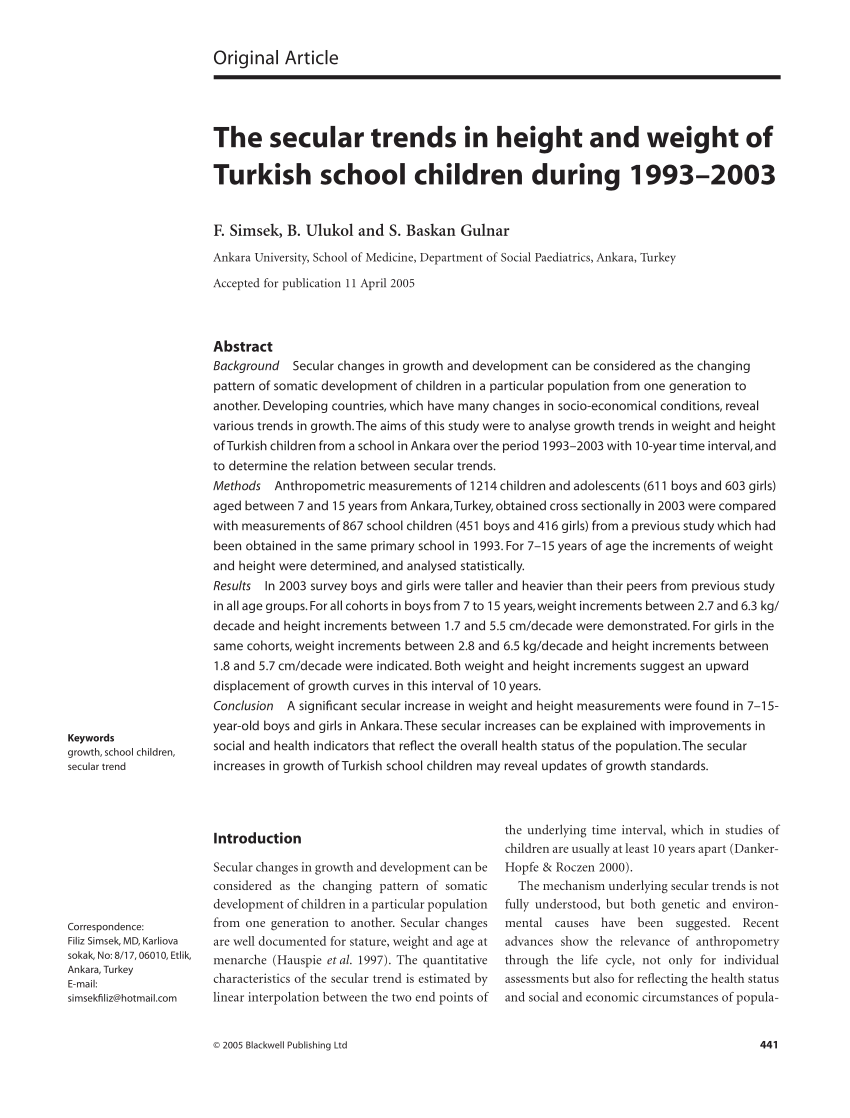
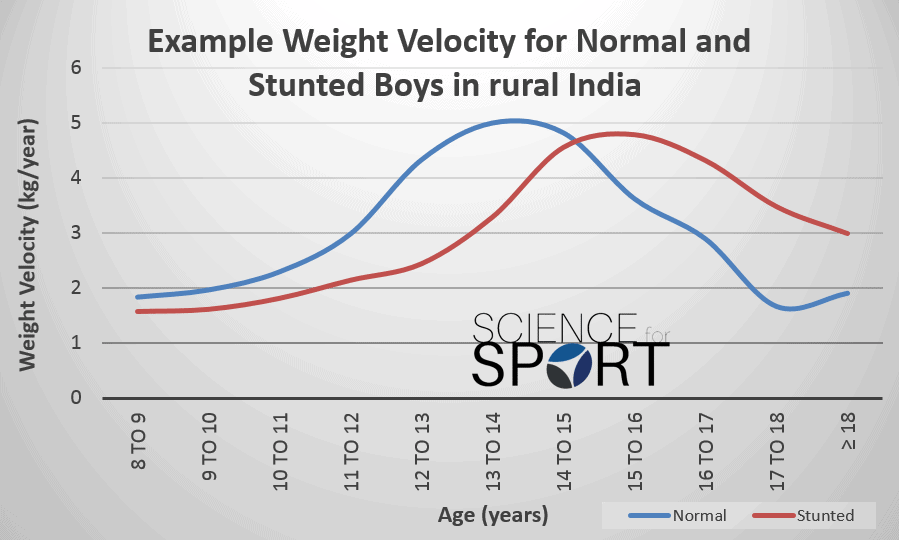
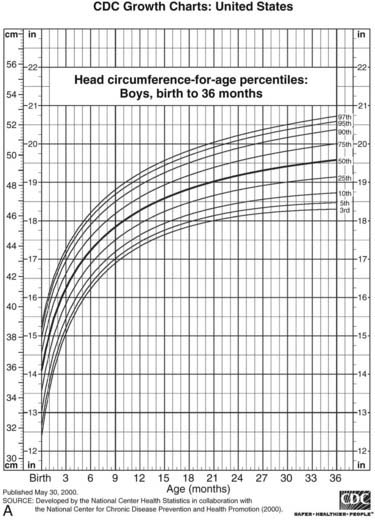
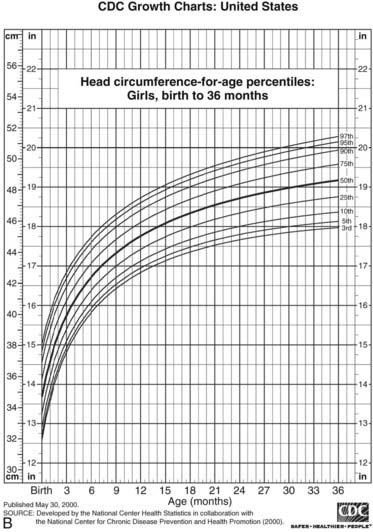
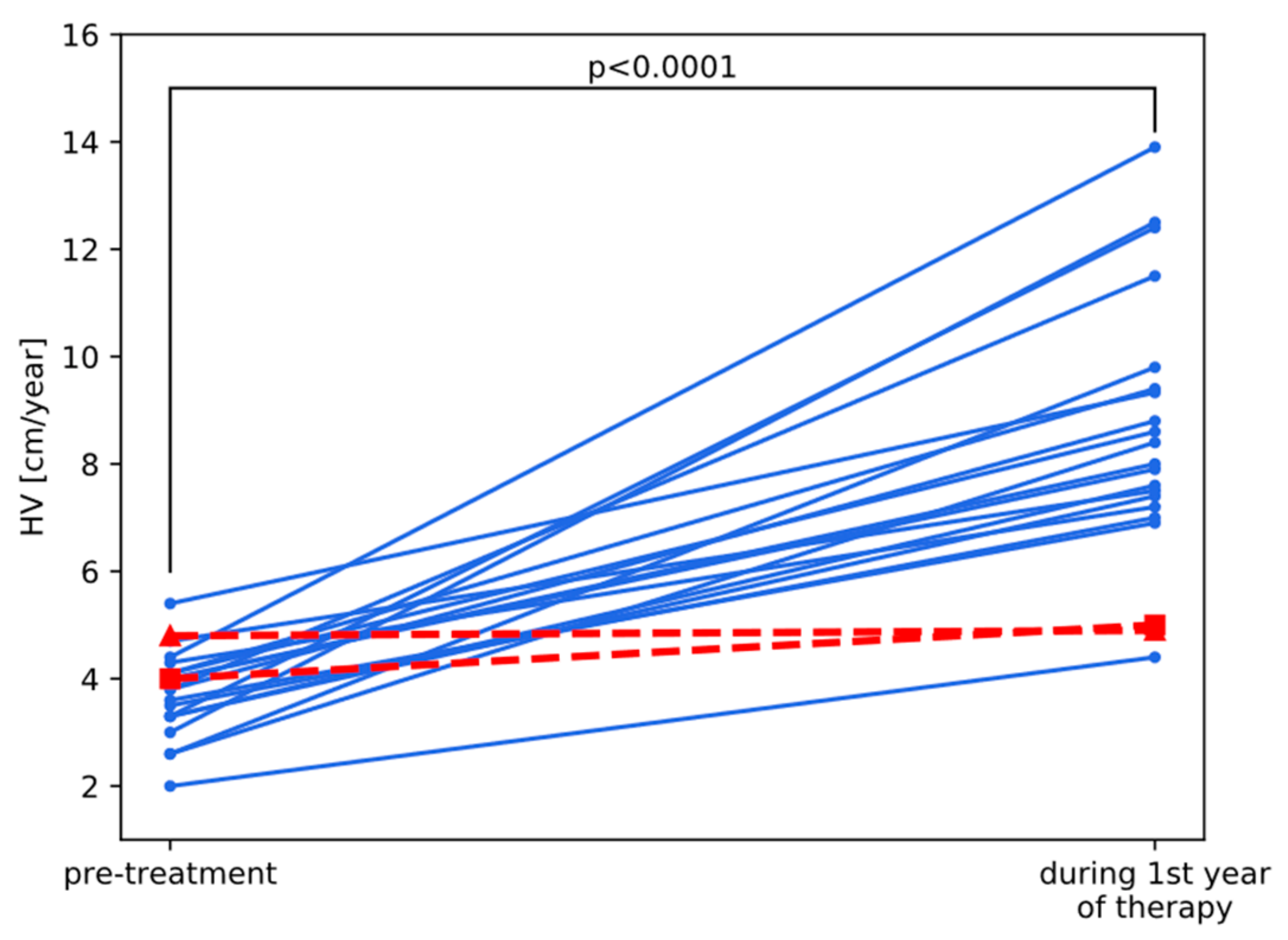
Familial and environmental determinants of early postnatal growth include gestational age at delivery birth size parental heights socioeconomic status and breastfeeding. Median z score for weight was 07 at birth 16 before bidirectional cavopulmonary shunt bcps 07 before fontan procedure and 07 after fontan procedurea significant decline in z scores for weight was seen before bcps which was reversed after the hemi fontan and stabilized after fontan procedurethe z scores for weight before the bcps were lower in patients with. 61 genes on the y chromosome seem to enhance stature commencing in antenatal life 6162 and the x chromosome carries genetic. Growth differences between children with low risk scd and controls were non significant. The most important tools for assessing somatic growth are growth charts which recently have been modified and published by the national center for health statistics. Both decrease men a lot more than women.
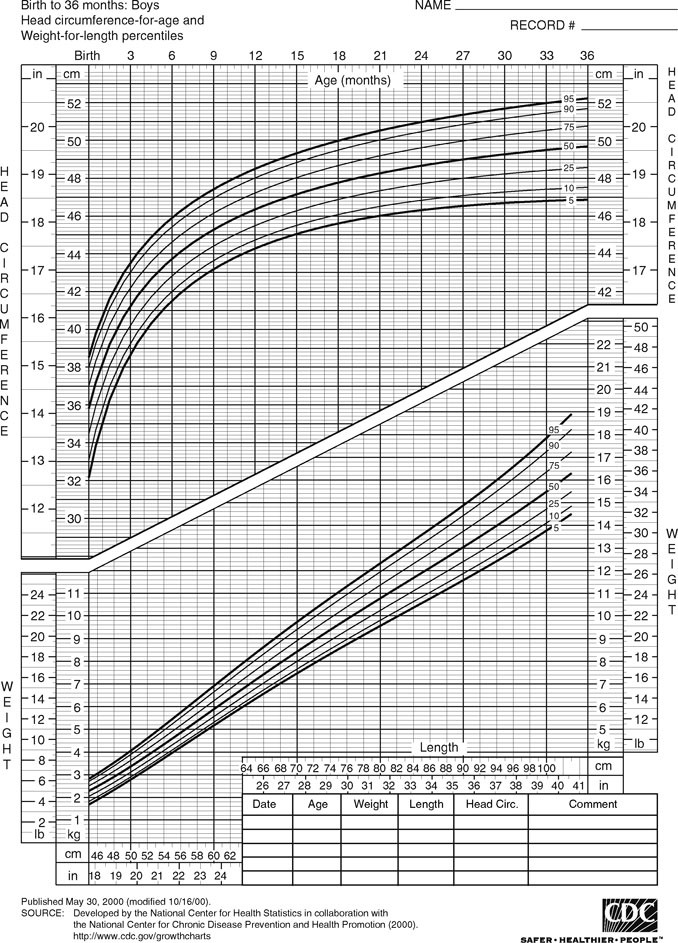
Somatic growth indices and cognitive outcomes. Controls had significantly higher mean height for age weight for age and bmi for age than those with high risk scd. Growth and cognitive measures showed variability across levels of scd status. 17 genetic determinants exist for both postnatal and prenatal growth. Somatic growth study guide by dcrawford90 includes 49 questions covering vocabulary terms and more. When is the peak height and weight growth peak height is before birth peak weight is shortly after birth.
Corollaries to the hypotheses are 1 somatic growth rate can influence the otolithfish size relationship 2 intraspecific variation in otolith scaling might be used to predict past differences in somatic growth rate and 3 there is a biological rationale for the use of otolith size and fish size as predictors in age estimation. These charts include height weight and head circumference for age with one set for children up to 36 months and a second set for children ages 2 to 18 years. Quizlet flashcards activities and games help you improve your grades.